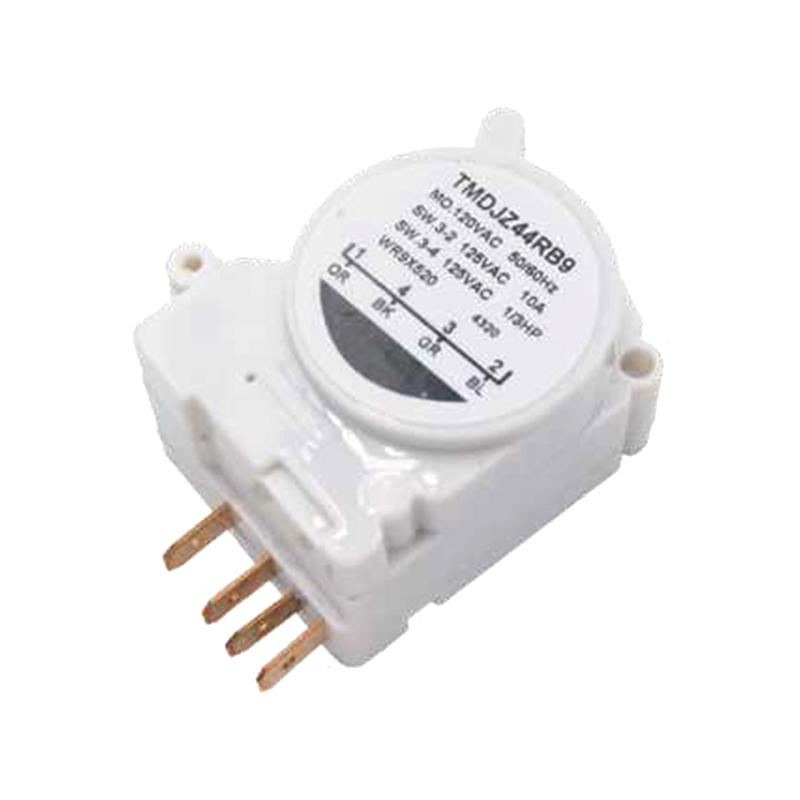
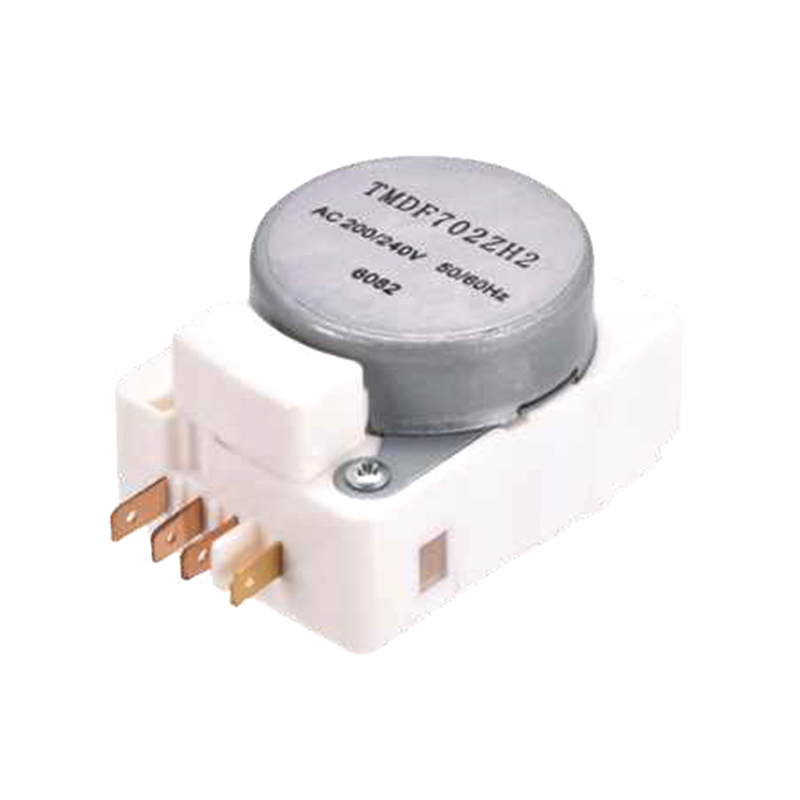
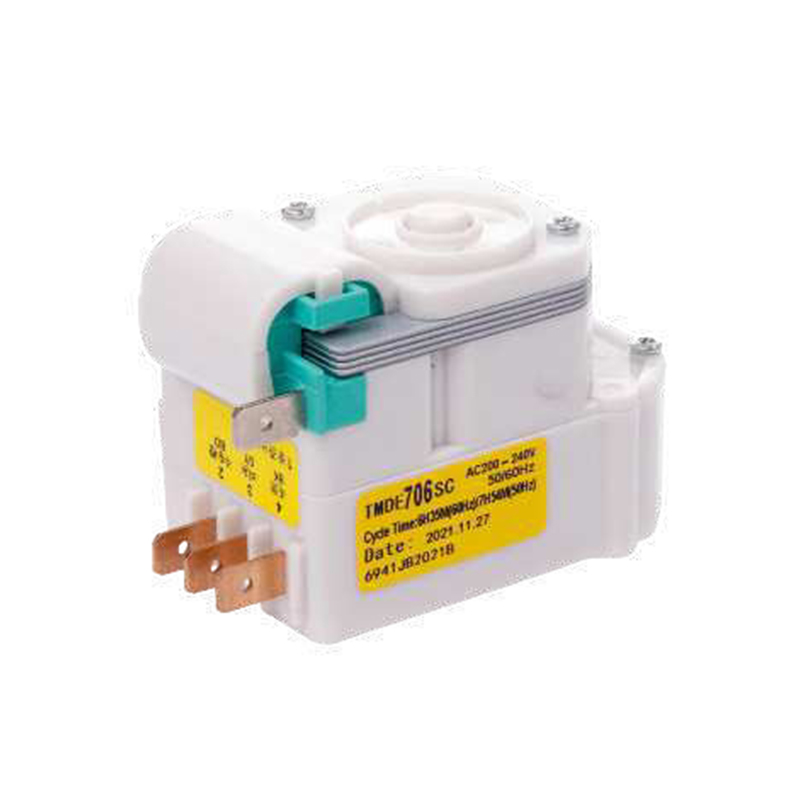
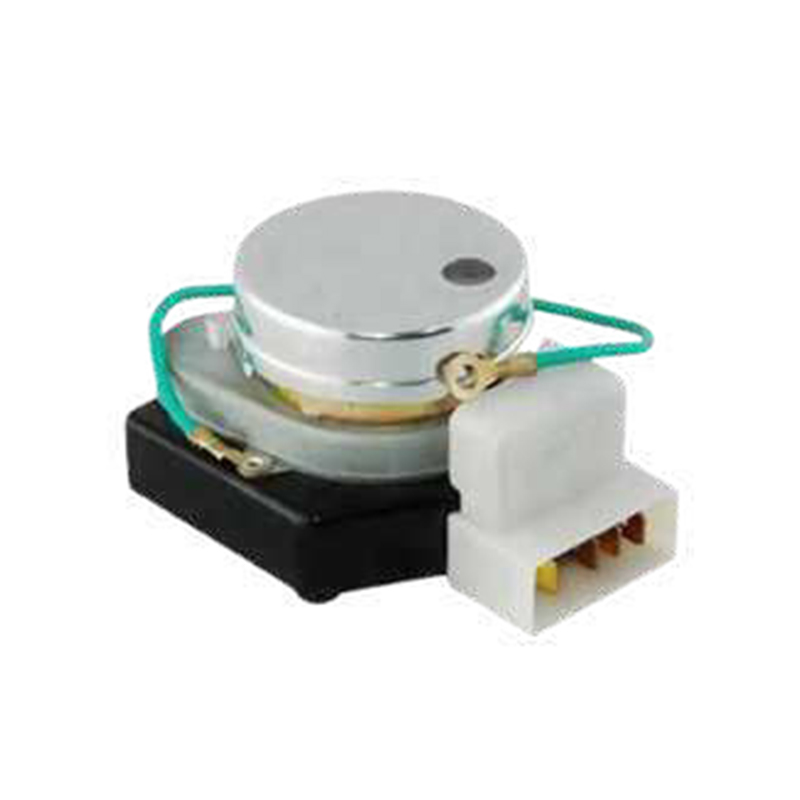
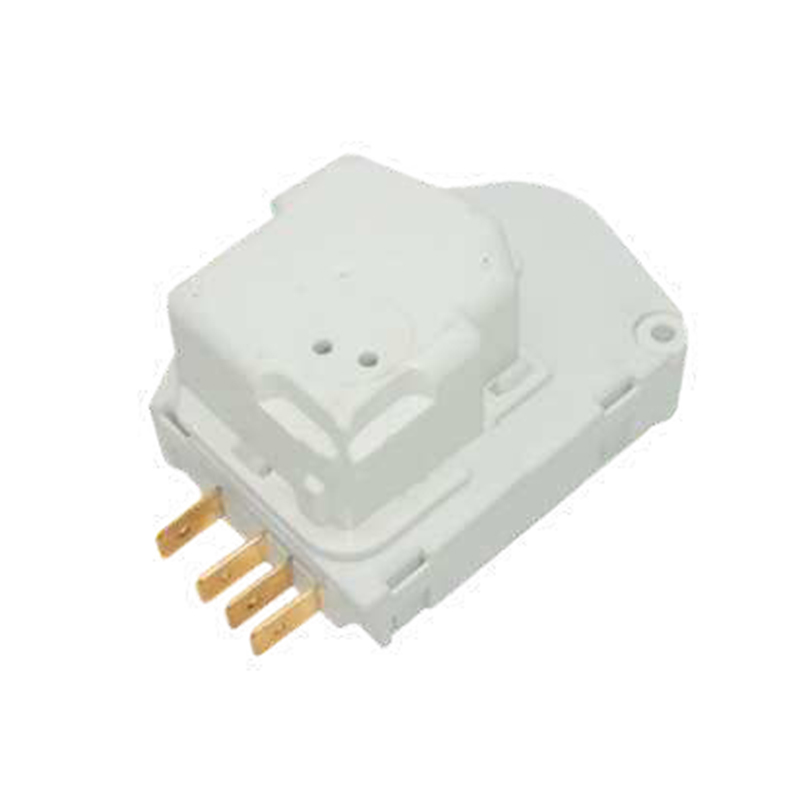
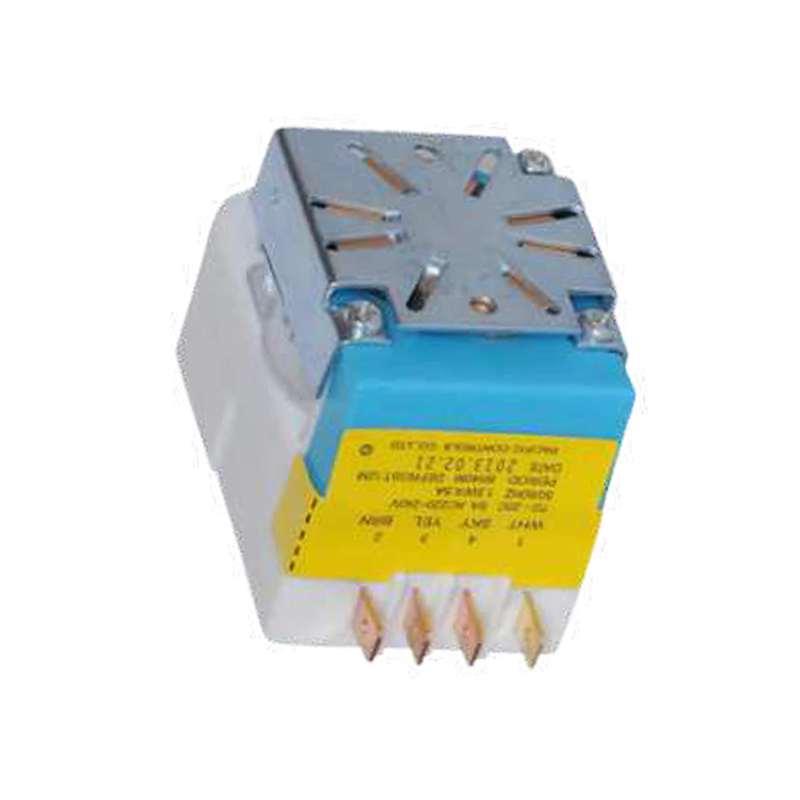
What energy efficiency benefits can using a defrost timer bring to home appliances?
Using a defrost timer can bring the following energy efficiency benefits to home appliances:
Energy saving and consumption reduction: Regular automatic defrosting can prevent frost accumulation, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the refrigerator or freezer. Excessive frost will increase the burden on the compressor and increase its power consumption. Timed defrosting can keep the equipment in optimal working condition and reduce power consumption.
Extend equipment life: Defrost timers can reduce overheating and wear of equipment, thereby extending the service life of refrigerators or freezers. Timely defrosting helps to keep the cooling system running normally and reduce the probability of failure.
Improve cooling efficiency: When frost accumulates on the cooler, it will cause the cooling effect to decrease. Using a defrost timer can ensure that the cooler always works efficiently and provides better cooling performance.
Reduce maintenance costs: Regular defrosting can reduce the frequency of manual frost cleaning by users, reducing maintenance costs. Timers can automate this process and reduce users' labor and time costs.
Keep food fresh: The accumulation of frost may affect the temperature distribution in the refrigerator, causing some areas to be too cold or too hot. Regular defrosting keeps the internal temperature uniform, ensuring that food stays at its best.
Improves air circulation: Frost accumulation can block air circulation, resulting in uneven distribution of cold air. Defrost timers can help maintain good air circulation, thereby improving cooling effects.
Prevents condensation accumulation: Proper defrosting prevents condensation accumulation, which not only helps keep the internal environment dry, but also reduces the growth of bacteria and mold.
Improves user experience: When a refrigerator or freezer is operating properly and efficiently, the user experience will be greatly improved, without having to worry about equipment performance degradation or frequent maintenance.
Smart home compatibility: Modern defrost timers can often integrate with smart home systems to optimize energy efficiency through intelligent control, allowing users to monitor and adjust equipment status at any time.
Reduce noise: By keeping the equipment operating normally, defrost timers can reduce the noise caused by equipment overheating and malfunctioning due to frost accumulation.
How to choose the right defrost timer for your equipment? What key parameters need to be considered?
There are several key parameters to consider when choosing a defrost timer for your appliance:
Compatibility: Make sure the defrost timer you choose is compatible with your model of refrigerator or freezer. Check the manufacturer's recommendations or specifications to confirm that the timer will work with your appliance.
Timer Types:
Mechanical timers: They are generally less expensive, simple to operate, and suitable for basic needs.
Electronic timers: They are more advanced and generally have more precise time control and programmable features, suitable for users who need more flexibility.
Time Setting Range: Check the timer's time setting range and choose one that can meet your appliance's defrost frequency needs. Generally speaking, defrost intervals between 6 and 12 hours are common settings.
Temperature Sensing: Some high-end timers are equipped with temperature sensors that can automatically adjust the defrost time based on the temperature inside the appliance. This feature can improve energy efficiency and ensure that the appliance is operating at optimal conditions.
Power Requirements: Confirm the timer's power requirements (such as voltage and wattage) to ensure that they match your appliance's power system to avoid potential electrical problems.
Use Environment: Consider the environment in which your appliance will be used (such as temperature and humidity) and choose a durable defrost timer that can withstand environmental factors.
Installation ease: Make sure the timer is easy to install without too many tools or specialized skills. Some timers may require more complex wiring, which needs to be known in advance.
Features:
Programming: Some timers allow you to set different defrost programs to suit different usage needs.
Fault indication: Some high-end models are equipped with fault indicators or alarms to alert users to problems with the equipment.

 English
English Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى