- Home
- About Us
- Product
- Capacitor
- Air-Conditioner Parts
- Compressor
- Universal A/C Control System & Remote
- Temperature Controller
- Contactor & Transformer
- Relay & Overload & Delay Timer
- Indoor And Outdoor Air Conditioning Motor
- Defrost Timer
- Thermostat Guard
- Select Switch
- Fan Blade
- Air Conditioner Bracket
- A/C Flow Deflector & A/C Service Bag
- High Pressure Washer
- Charging Valve & Capillary & Wave Tube
- All A/C Brands Sensor
- Insulation tuber
- Refrigerator Parts
- Refrigeration Parts
- Axial Fan
- Microcomputer Temperature Control
- Voltage Protector
- Vacuum Pump & Refrigerant Recovery Unit & Scale
- Brass & Copper Fitting
- Installation Material
- PVC Air Curtain
- Condensate Drain Pump
- Refrigerant
- Copper Tube
- Filter Drier & Oil Separator For Refrigeration System
- Vibration Absorber
- Control Valve & Fitting & Component
- Manifold Gauge
- Thermometer
- Air Curtain
- Condenser Unit
- Condensing Unit
- AC Cooling Fan
- Refrigerant Leak Detector
- Latch & Hinge
- Washing Machine Parts
- Home Appliances Parts
- Instruments&Tools
- Resources
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Product
- Capacitor
- Air-Conditioner Parts
- Compressor
- Universal A/C Control System & Remote
- Temperature Controller
- Contactor & Transformer
- Relay & Overload & Delay Timer
- Indoor And Outdoor Air Conditioning Motor
- Defrost Timer
- Thermostat Guard
- Select Switch
- Fan Blade
- Air Conditioner Bracket
- A/C Flow Deflector & A/C Service Bag
- High Pressure Washer
- Charging Valve & Capillary & Wave Tube
- All A/C Brands Sensor
- Insulation tuber
- Refrigerator Parts
- Refrigeration Parts
- Axial Fan
- Microcomputer Temperature Control
- Voltage Protector
- Vacuum Pump & Refrigerant Recovery Unit & Scale
- Brass & Copper Fitting
- Installation Material
- PVC Air Curtain
- Condensate Drain Pump
- Refrigerant
- Copper Tube
- Filter Drier & Oil Separator For Refrigeration System
- Vibration Absorber
- Control Valve & Fitting & Component
- Manifold Gauge
- Thermometer
- Air Curtain
- Condenser Unit
- Condensing Unit
- AC Cooling Fan
- Refrigerant Leak Detector
- Latch & Hinge
- Washing Machine Parts
- Home Appliances Parts
- Instruments&Tools
- Resources
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu

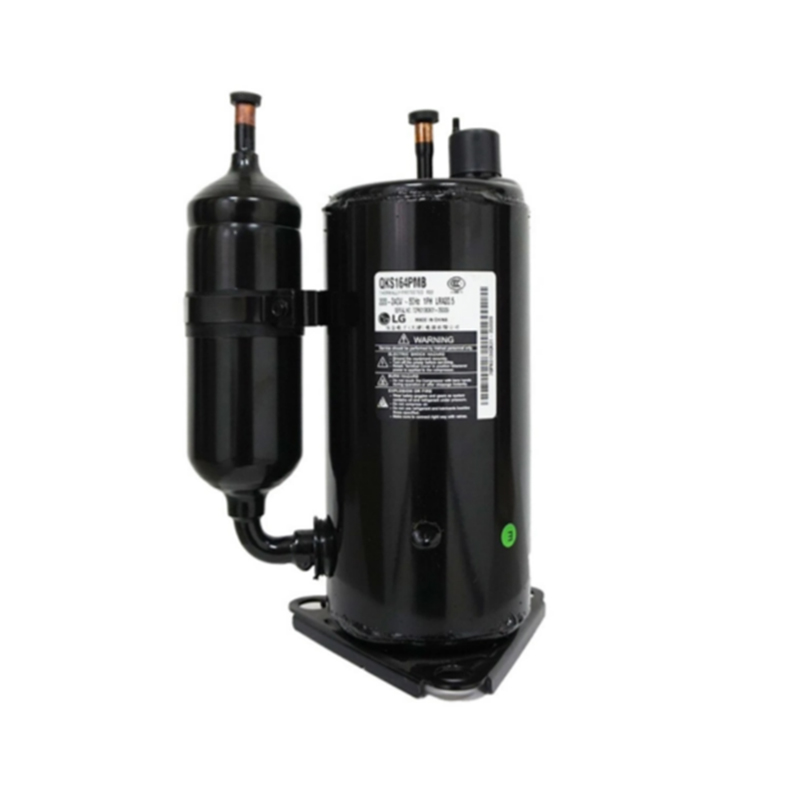
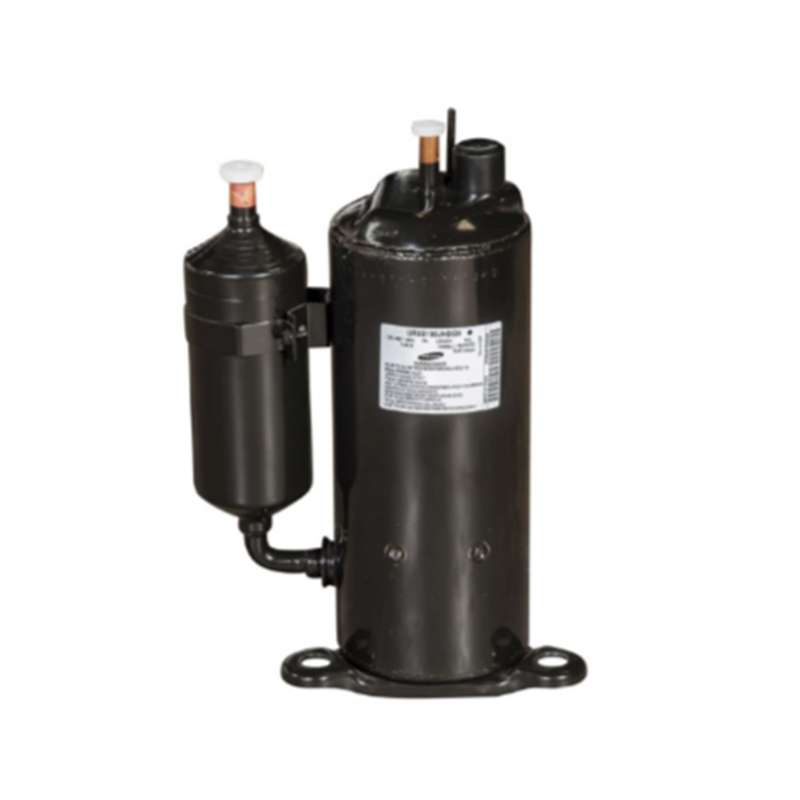
Compressor for Air Conditioner & Refrigerator: A Comprehensive Guide
Posted by Admin | 21 Nov
How Does a Compressor Work in an Air Conditioner?
In an air conditioner, the compressor is responsible for removing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside. Here’s how it works:
Evaporation: The refrigerant enters the evaporator coil inside the air handler as a low-pressure, cold liquid. As air is blown over the coil, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air and evaporates into a low-pressure gas.
Compression: The low-pressure refrigerant gas is then drawn into the compressor. The compressor compresses the gas, raising its pressure and temperature.
Condensation: The high-pressure, hot gas flows into the condenser coil located outside. Here, it releases its heat into the outside air and condenses back into a high-pressure liquid.
Expansion: The refrigerant is then allowed to expand through an expansion valve, which causes it to cool down further, and the cycle repeats.
This continuous cycle keeps the temperature in the room cool and comfortable.
How Does a Compressor Work in a Refrigerator?
The refrigeration cycle in a refrigerator is similar to that of an air conditioner but operates at colder temperatures to keep food and beverages cool. Here’s a breakdown:
Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs heat from inside the refrigerator as it evaporates in the evaporator coils. This process cools down the interior of the fridge.
Compression: The low-pressure refrigerant gas is sucked into the compressor, which compresses it, raising its temperature and pressure.
Condensation: The high-pressure refrigerant gas is sent to the condenser coils (typically located at the back or bottom of the fridge). Here, the gas cools and condenses into a liquid form.
Expansion: The refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, where it cools down further before entering the evaporator coil to start the cycle again.
This refrigeration process continues, maintaining the low temperature needed to keep food cold and fresh.
Types of Compressors Used in Air Conditioners and Refrigerators
There are different types of compressors used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, each with its own benefits and suitability for specific applications:
Reciprocating Compressor:
The most common type of compressor in both air conditioners and refrigerators.
It uses a piston to compress the refrigerant gas inside a cylinder.
Known for its reliability and efficiency in small to medium-sized systems.
It is often used in home appliances, such as refrigerators and small air conditioners.
Rotary Compressor:
Utilizes a rotary mechanism instead of a piston.
Smaller, quieter, and more energy-efficient than reciprocating compressors.
Often found in compact air conditioning units and refrigerators.
Scroll Compressor:
Features two interleaved spiral-shaped scrolls, one stationary and the other orbiting.
Offers higher efficiency and quieter operation.
Used in larger air conditioning systems, heat pumps, and refrigeration applications.
Screw Compressor:
Uses two interlocking helical screws to compress the refrigerant gas.
Known for handling larger volumes of refrigerant and working in commercial or industrial applications.
Typically found in larger-scale air conditioning systems or commercial refrigeration units.
Importance of a Good Compressor
A high-quality compressor is essential for the efficient functioning of both air conditioners and refrigerators. The compressor determines how well the system maintains the desired temperature. If the compressor fails, the cooling system will not work effectively, leading to issues such as the inability to cool air or preserve food properly.
Efficiency: A well-functioning compressor ensures that the system works efficiently, using the least amount of energy to provide maximum cooling.
Longevity: A reliable compressor ensures the system lasts longer without requiring frequent repairs or replacements.
Cost Savings: Efficient compressors consume less power, reducing electricity costs in the long run.
Signs of a Failing Compressor
A compressor can fail for several reasons, including electrical issues, mechanical wear, or refrigerant leaks. Common signs of a failing compressor include:
No cooling: The air conditioner or refrigerator may fail to cool the space or maintain the desired temperature.
Strange noises: Unusual sounds such as buzzing, clicking, or rattling may indicate that the compressor is malfunctioning.
Increased energy consumption: If the compressor is working harder than usual, it can lead to higher electricity bills.
Overheating: If the compressor overheats, it can cause the system to shut down or lead to permanent damage.

Efficient charging, stable output, capacitor, thefirst choice for electric drive.
- Address: FLAT/RM A 12/FZJ300 .300 LOCKHART ROAD WANCHAI HONGKONG
- Phone/WhatsApp: +86-13865318126
- Email: [email protected]
If you have anything to consult, you canfollow us, we will contact you as soon aspossible
Copyright © HONG KONG KING COOL LIMITED All Rights Reserved. Custom HVAC Parts & Accessories Suppliers